A type of thermoset insulation is a material that has undergone irreversible chemical changes upon curing, resulting in a rigid, cross-linked structure. These materials exhibit exceptional thermal and electrical insulation properties, making them ideal for a wide range of applications.
Thermoset insulation finds applications in various industries, including electrical, aerospace, and industrial equipment. Its high temperature resistance, durability, and resistance to chemicals and solvents make it a preferred choice for demanding environments.
Introduction to Thermoset Insulation
Thermoset insulation is a type of polymeric material that undergoes an irreversible chemical change upon curing, forming a rigid and cross-linked structure. It possesses exceptional thermal, electrical, and mechanical properties, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Examples of applications include electrical wiring, aerospace components, and industrial equipment.
Types of Thermoset Insulation
| Material | Properties | Applications | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy | High strength, electrical resistance, chemical resistance | Electrical insulation, adhesives | Durable, versatile |
| Phenolic | Flame retardant, low thermal conductivity | Electrical components, automotive parts | Lightweight, cost-effective |
| Polyester | High temperature resistance, mechanical strength | Aerospace components, marine applications | Dimensionally stable, good electrical properties |
| Silicone | Extreme temperature resistance, flexibility | Electronics, medical devices | Biocompatible, non-toxic |
Properties of Thermoset Insulation
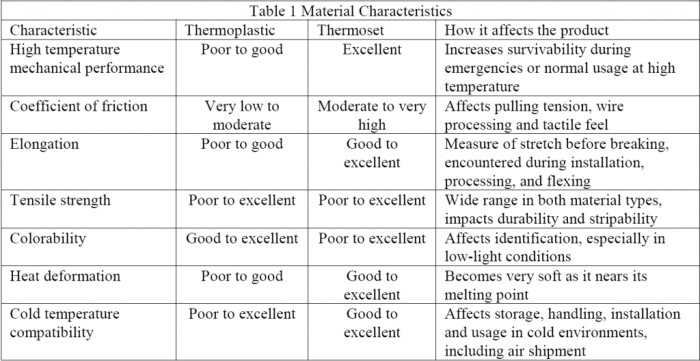
- Thermal conductivity:Low thermal conductivity, providing excellent insulation properties.
- Electrical resistance:High electrical resistance, making it suitable for electrical applications.
- Mechanical strength:High mechanical strength, ensuring durability and resistance to wear.
- Chemical resistance:Resistant to a wide range of chemicals and solvents, enhancing durability.
Applications of Thermoset Insulation
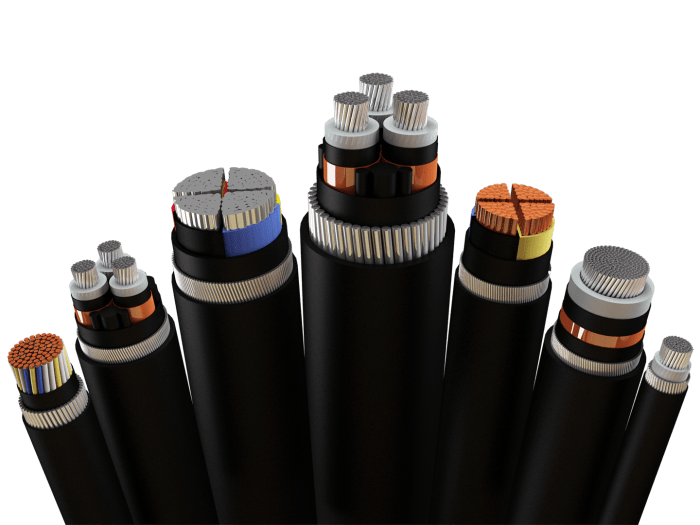

- Electrical wiring insulation
- Aerospace components (e.g., radomes, insulation for electronic systems)
- Industrial equipment insulation (e.g., motors, transformers)
- Automotive parts (e.g., electrical connectors, insulation for wiring harnesses)
- Electronic devices (e.g., printed circuit boards, semiconductor packaging)
Advantages and Disadvantages of Thermoset Insulation: A Type Of Thermoset Insulation Is
Advantages, A type of thermoset insulation is
- High temperature resistance, enabling use in demanding applications.
- Durability and long lifespan, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
- Resistance to chemicals and solvents, ensuring integrity in harsh environments.
Disadvantages
- Limited flexibility, making it less suitable for applications requiring flexibility.
- Difficulty in repair, as thermoset materials are typically difficult to modify or repair once cured.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the key properties of thermoset insulation?
Thermoset insulation is characterized by its high thermal conductivity, electrical resistance, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance.
What are the advantages of using thermoset insulation?
Advantages of thermoset insulation include high temperature resistance, durability, and resistance to chemicals and solvents.
What are the disadvantages of thermoset insulation?
Disadvantages of thermoset insulation include limited flexibility and difficulty in repair.