Delving into bioflix activity: membrane transport — diffusion, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative, with gaya akademik dengan tone otoritatif that is both engaging and thought-provoking from the very first sentence. The topic of membrane transport and diffusion lies at the heart of cellular biology, governing the movement of substances across cell membranes and playing a crucial role in a myriad of biological processes.
This exploration will provide a comprehensive understanding of the concept, its types, influencing factors, biological significance, medical applications, and experimental techniques, equipping readers with a profound knowledge of this fundamental aspect of life.
The subsequent paragraphs will delve into the intricacies of membrane transport and diffusion, shedding light on the mechanisms that underpin the movement of molecules across cell membranes. We will explore the different types of diffusion, including simple, facilitated, and osmosis, and examine the factors that influence the rate of diffusion, such as concentration gradient, temperature, and surface area.
Furthermore, we will investigate the crucial role of membrane transport in various biological processes, such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and cell signaling.
1. Definition and Overview
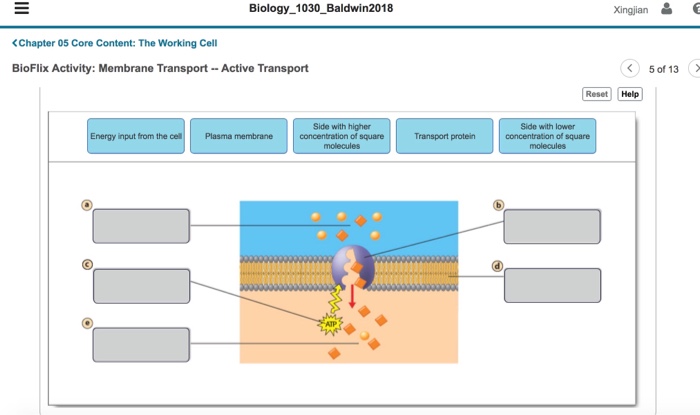
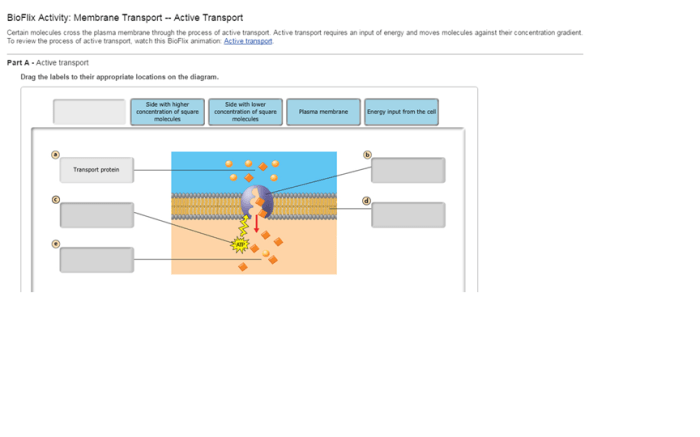
Membrane transport is the movement of molecules across biological membranes. The cell membrane, a phospholipid bilayer, regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell, maintaining cellular homeostasis and facilitating various biological processes.
2. Types of Diffusion, Bioflix activity: membrane transport — diffusion
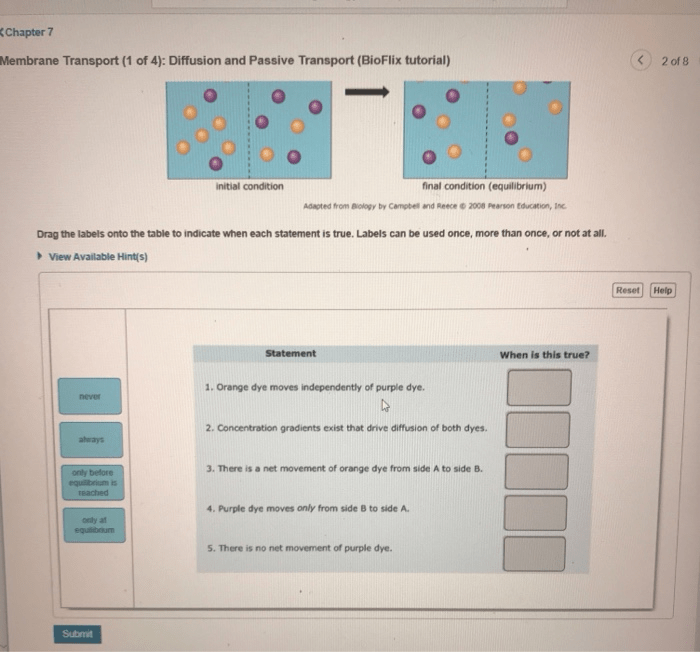
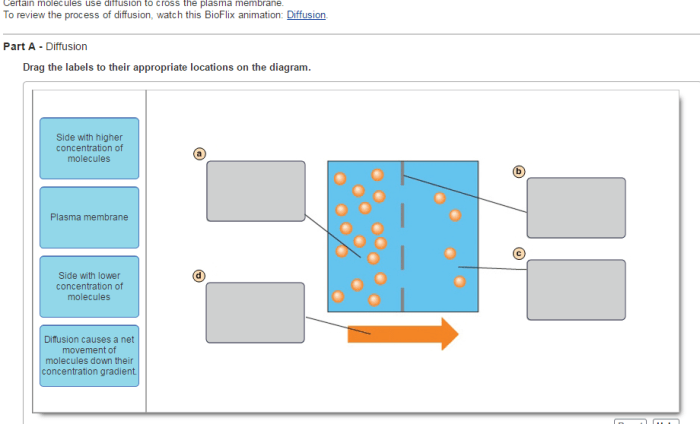
Diffusion is a passive transport process that involves the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. There are three main types of diffusion:
- Simple diffusion: The direct movement of small, nonpolar molecules across the lipid bilayer.
- Facilitated diffusion: The movement of polar molecules or ions across the membrane with the help of carrier proteins.
- Osmosis: The movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
3. Factors Affecting Diffusion
The rate of diffusion is influenced by several factors:
- Concentration gradient: The difference in concentration between the two areas.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of molecules, leading to faster diffusion.
- Surface area: A larger surface area allows for more molecules to move across the membrane.
| Factor | Effect on Diffusion Rate |
|---|---|
| Concentration gradient | Higher gradient leads to faster diffusion |
| Temperature | Higher temperature leads to faster diffusion |
| Surface area | Larger surface area leads to faster diffusion |
4. Role in Biological Processes
Membrane transport plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including:
- Nutrient uptake: Transport of nutrients into the cell for energy production and cellular functions.
- Waste removal: Removal of metabolic waste products from the cell.
- Cell signaling: Transport of signaling molecules across the membrane to trigger cellular responses.
5. Medical Applications
Understanding membrane transport principles has led to advancements in medical treatments, such as:
- Drug delivery: Designing drug delivery systems that can effectively target and deliver drugs to specific tissues.
- Dialysis: Using artificial membranes to remove waste products from the blood in patients with kidney failure.
6. Experimental Techniques
Various experimental techniques are used to study membrane transport:
- Tracer studies: Using radioactive or fluorescently labeled molecules to track their movement across membranes.
- Patch-clamp methods: Using micropipettes to record electrical currents through ion channels in cell membranes.
Questions and Answers: Bioflix Activity: Membrane Transport — Diffusion
What is the significance of membrane transport in biological systems?
Membrane transport is crucial for the survival and proper functioning of biological systems. It enables the uptake of essential nutrients, the removal of waste products, and the maintenance of cellular homeostasis. Without efficient membrane transport, cells would be unable to perform their vital functions, leading to cellular dysfunction and ultimately organismal failure.
How does the rate of diffusion vary with temperature?
The rate of diffusion increases with increasing temperature. This is because higher temperatures provide molecules with more kinetic energy, allowing them to move more rapidly and overcome the energy barrier required for diffusion to occur.
What is the role of facilitated diffusion in biological processes?
Facilitated diffusion plays a critical role in the transport of molecules that cannot passively diffuse across cell membranes due to their size or charge. It involves the use of specific membrane proteins that bind to the molecules and facilitate their movement across the membrane, down their concentration gradient.