As a physical count of merchandise inventory on June 30 reveals significant discrepancies, this comprehensive analysis delves into the potential reasons for these variations, explores the impact on financial statements, and provides valuable insights into effective inventory management practices.
Inventory discrepancies can arise from various factors, including human error, theft, or outdated records. Understanding the causes of these discrepancies is crucial for businesses to implement robust inventory control measures and ensure accurate financial reporting.
Inventory Discrepancies: A Physical Count Of Merchandise Inventory On June 30 Reveals
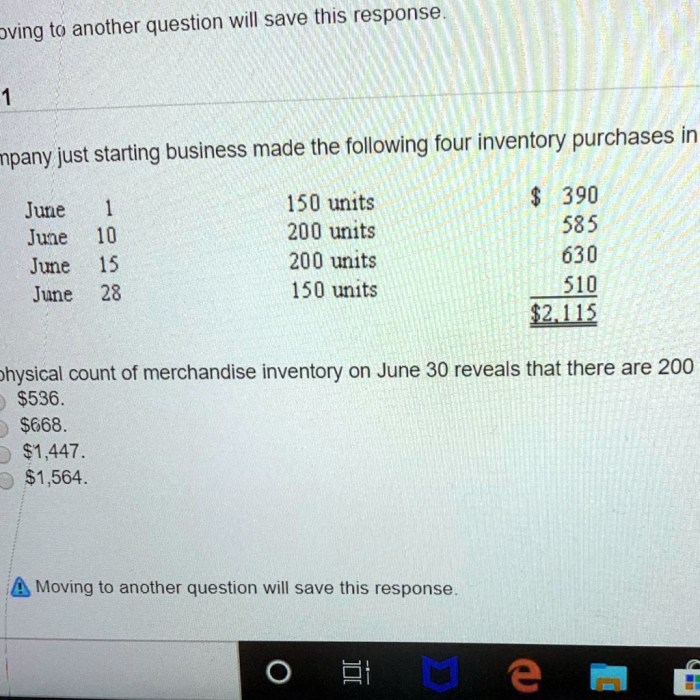
Physical inventory counts can reveal discrepancies between the physical count and the inventory records. These discrepancies can be caused by various factors, including errors in counting, recording, or theft.
Common Inventory Errors, A physical count of merchandise inventory on june 30 reveals
- Counting errors: Incorrectly counting the number of items in the inventory.
- Recording errors: Errors in transcribing or entering the inventory count into the records.
- Theft: Intentional removal of inventory items without authorization.
Impact on Financial Statements
Inventory discrepancies can significantly impact financial statements. An overstatement of inventory can lead to overstated assets and net income, while an understatement of inventory can lead to understated assets and net income.
Inventory Valuation
Inventory valuation methods determine the value of inventory on the balance sheet. Different valuation methods can result in different reported values for the same inventory.
Common Valuation Methods
- First-in, first-out (FIFO): Assumes that the oldest inventory items are sold first.
- Last-in, first-out (LIFO): Assumes that the most recently acquired inventory items are sold first.
- Weighted average cost: Calculates the average cost of all inventory items on hand.
Impact of Valuation Methods
The choice of valuation method can affect the reported value of inventory, which in turn can impact financial ratios and profitability.
Inventory Management
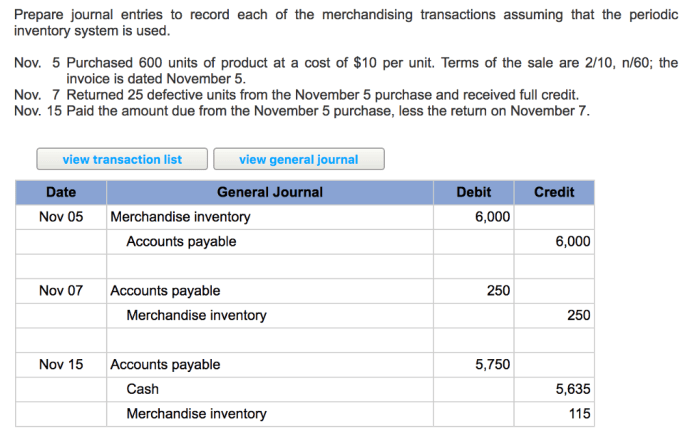
Effective inventory management is crucial for optimizing inventory levels, reducing costs, and improving customer service.
Key Principles
- Maintaining optimal inventory levels: Holding enough inventory to meet customer demand without overstocking.
- Minimizing inventory costs: Reducing storage, handling, and other inventory-related expenses.
- Improving customer service: Ensuring that products are available when customers need them.
Inventory Management Techniques
- Just-in-time inventory: Ordering inventory only when it is needed for production or sale.
- Safety stock: Maintaining a buffer of inventory to prevent stockouts.
- Vendor-managed inventory: Allowing suppliers to manage inventory levels.
Benefits of Effective Inventory Management
- Reduced inventory costs
- Improved customer service
- Increased profitability
Inventory Control

Inventory control systems are designed to prevent theft, fraud, and unauthorized access to inventory.
Methods of Inventory Control
- Physical safeguards: Physical barriers, such as fences and security cameras, to prevent unauthorized access.
- Inventory tracking systems: Software or manual systems to track inventory movements and locations.
- Inventory audits: Regular reviews of inventory to verify accuracy and prevent theft.
Importance of Inventory Control
Effective inventory control is essential for protecting inventory assets and ensuring the accuracy of financial records.
FAQ Compilation
What are the common causes of inventory discrepancies?
Inventory discrepancies can result from human error during counting, theft, receiving errors, shipping errors, or outdated inventory records.
How do inventory discrepancies impact financial statements?
Inventory discrepancies can lead to overstatement or understatement of inventory value, which can affect the accuracy of financial statements, such as the balance sheet and income statement.
What are the key principles of effective inventory management?
Effective inventory management involves establishing accurate inventory records, implementing inventory control systems to prevent theft and fraud, and optimizing inventory levels to meet customer demand while minimizing holding costs.