The periodic table worksheet answers provide a comprehensive overview of the fundamental principles and applications of the periodic table. This guide delves into the structure, properties, and uses of the periodic table, empowering learners with a deeper understanding of the behavior and characteristics of elements.
The periodic table is an invaluable tool for chemists, physicists, and other scientists, offering insights into the chemical and physical properties of elements. It serves as a roadmap to predict the reactivity, bonding behavior, and physical state of elements, enabling researchers to make informed decisions and advance scientific discoveries.
The Periodic Table Basics: The Periodic Table Worksheet Answers
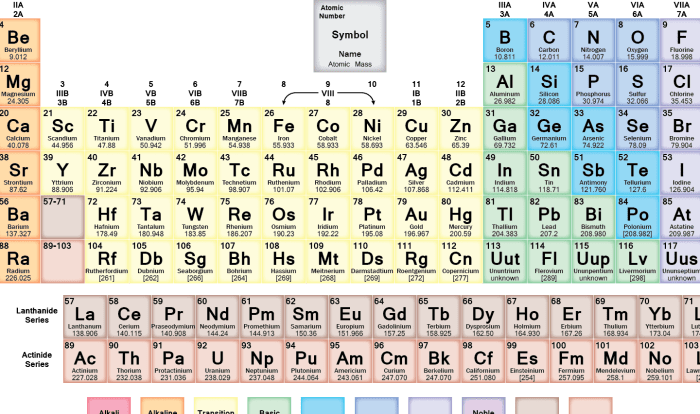
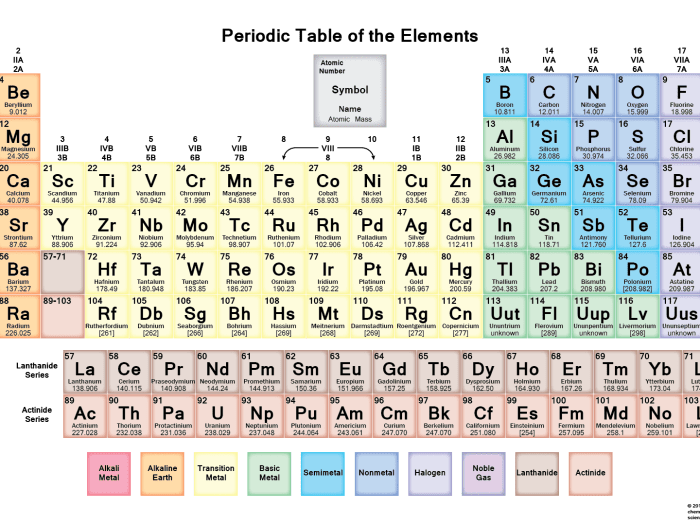
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties.
The table has 18 vertical columns, called groups, and 7 horizontal rows, called periods. Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties, while elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
Element Symbols, Atomic Numbers, and Atomic Masses
Each element in the periodic table is represented by a unique chemical symbol, which is typically one or two letters. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in its nucleus, and is written as a subscript to the left of the element symbol.
The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average mass of all the isotopes of that element, and is written as a superscript to the left of the element symbol.
| Element Symbol | Atomic Number | Atomic Mass |
|---|---|---|
| H | 1 | 1.008 |
| He | 2 | 4.0026 |
| Li | 3 | 6.941 |
| Be | 4 | 9.0122 |
| B | 5 | 10.811 |
Trends in Atomic Radius, Ionization Energy, and Electronegativity
As you move down a group in the periodic table, the atomic radius of the elements increases. This is because the number of electron shells increases, and the electrons are further away from the nucleus.
As you move across a period in the periodic table, the ionization energy of the elements increases. This is because the number of protons in the nucleus increases, and the electrons are held more tightly.
As you move across a period in the periodic table, the electronegativity of the elements increases. This is because the number of protons in the nucleus increases, and the electrons are more strongly attracted to the nucleus.
The Periodic Table and Chemical Properties

The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. It can be used to predict the chemical properties of elements based on their position in the table.
Identifying Elements with Similar Properties
Elements in the same group (vertical column) of the periodic table have similar chemical properties. This is because they have the same number of valence electrons, which are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom. Valence electrons determine the chemical reactivity of an element.
- For example, all alkali metals (Group 1) are highly reactive and form 1+ ions.
- All halogens (Group 17) are highly reactive and form 1- ions.
Chemical Reactivity
The periodic table can also be used to predict the chemical reactivity of elements. In general, elements become more reactive as you move down a group and from right to left across a period (horizontal row).
- For example, fluorine (F) is the most reactive nonmetal, while helium (He) is the least reactive.
- Potassium (K) is more reactive than sodium (Na), and chlorine (Cl) is more reactive than fluorine (F).
The Periodic Table and Physical Properties

The periodic table provides valuable insights into the physical properties of elements, allowing for predictions and identification of elements with similar characteristics. By understanding the trends and patterns within the table, scientists can determine various physical properties, such as melting point, boiling point, density, and electrical conductivity.
Predicting Physical Properties
The periodic table’s organization based on atomic number and electron configuration enables the prediction of physical properties. Elements within the same group (vertical columns) tend to exhibit similar physical properties due to the same number of valence electrons. For example, all alkali metals (Group 1) are highly reactive, have low melting points, and are good conductors of electricity.
Identifying Elements with Similar Physical Properties, The periodic table worksheet answers
The periodic table also aids in identifying elements with similar physical properties. For instance, elements in the same period (horizontal rows) generally have similar atomic radii and ionization energies. This knowledge helps in selecting suitable elements for specific applications based on their desired physical properties.
Relationship between Periodic Table and Physical State
The periodic table further reveals the relationship between an element’s position and its physical state at room temperature. Metals are typically found on the left side of the table, while nonmetals occupy the right side. Elements in the middle exhibit properties of both metals and nonmetals, known as metalloids.
The Periodic Table and Applications
The periodic table is a powerful tool that has revolutionized the way we understand and use elements. It is a comprehensive arrangement of all known elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
The periodic table finds applications in various fields of science and technology. It serves as a guide for predicting the properties of elements and their compounds, facilitating the development of new materials, medicines, and technologies. Additionally, the periodic table plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of elements in the environment.
Applications in Material Science
The periodic table is a valuable resource in material science. It helps scientists design and develop new materials with specific properties. For instance, by understanding the trends in atomic radii, electronegativity, and ionization energy across the periodic table, researchers can predict the strength, hardness, and electrical conductivity of various materials.
Applications in Medicine
The periodic table has significant applications in the field of medicine. It aids in the development of new drugs and treatments by providing insights into the interactions between elements and biological systems. For example, the discovery of penicillin, one of the most important antibiotics, was guided by the periodic table.
Applications in Environmental Science
The periodic table is essential for understanding the behavior of elements in the environment. It helps scientists assess the potential risks associated with environmental pollutants and develop strategies to mitigate their impact. For instance, the periodic table can be used to predict the solubility and mobility of heavy metals in soil and water, which is crucial for developing effective remediation strategies.
FAQ Corner
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
How can the periodic table be used to predict chemical properties?
The periodic table allows scientists to predict the chemical properties of an element based on its position within the table. Elements in the same group (vertical column) tend to have similar chemical properties due to their shared valence electron configuration.
What are some applications of the periodic table?
The periodic table finds applications in various fields, including chemistry, physics, materials science, and medicine. It is used to design new materials, develop pharmaceuticals, and understand the behavior of elements in the environment.